According to a major report, young people should pay attention to six important points to avoid falling victim to the growing cancer epidemic.
They should avoid excessive use of antibiotics, eat red meat no more than three times a week, wear condoms and avoid excessive alcohol consumption, said a major national cancer research organization.
Rising rates of many cancers in young people are front and center in the American Association for Cancer Research’s new annual report published last night.
Cancer is thought to be caused by a combination of your genes and your environment, but about 40 percent of all diagnosed cases can be traced back to one of these risk factors, the report it said. For example, cervical cancer is associated with the STD human papilloma virus.
Cancers starting in the US have been increasing since 1995, including colon, rectum, cervix, prostate, breast and endometrium.
The AACR report estimated that, annually, two million new cases of cancer will be diagnosed in the US by 2024.
Of these, about 4.2 percent will be in people between the ages of 18 and 50, who are typically considered too young to develop cancer.
Cancer is thought to be caused by an unfortunate combination of your genes and your environment.
However, ACCR scientists said that about 40 percent of all cases can be attributed to six different modifiable risk factors.
For young people, these include: unhealthy diet, obesity, chemicals in the environment, antibiotics, alcohol and sedentary behaviour.
For starters, only a quarter of adults and one in six high school children meet the CDC’s recommended physical activity guidelines.
The center says everyone should get 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as running, swimming or playing sports, and two days of muscle-strengthening exercise such as lifting metals or palates.
Less physical activity during adolescence is associated with an increased risk of cancer in adulthood.
The report also highlighted diet as a major cause of teenage cancer.
In particular, a diet based on red meat, highly processed foods and no fresh produce, are worried by AACR scientists.
These recommendations lead the group to say no more than three servings of red meat per week.
They also say that cooked meats such as hot dogs, bacon and salami should not be included in the regular diet as they are associated with the risk of contracting many diseases.
Teenagers and young adults tend to have less nutritious meals than older adults – they prefer the convenience found in fast food.
Forty-five percent of American adults reported eating fast food on a daily basis between 2013 and 2017 — compared to 37 percent of adults over 40.
“Reducing or eliminating the consumption of processed foods, fast food, and foods and beverages high in sugar is essential to curbing the obesity epidemic and reducing the burden of related cancers,” the report said.
They also recommend avoiding alcoholic beverages — such as soda, juice, canned coffee and energy drinks — that have added sugar. They have been linked to liver, colon cancer and diabetes.
Studies have shown that drinking one or more sugary drinks a day made someone 1.8 times more likely to develop liver cancer than those who did not.
In response to these findings, the AACR report highlighted solutions such as a sugar tax.

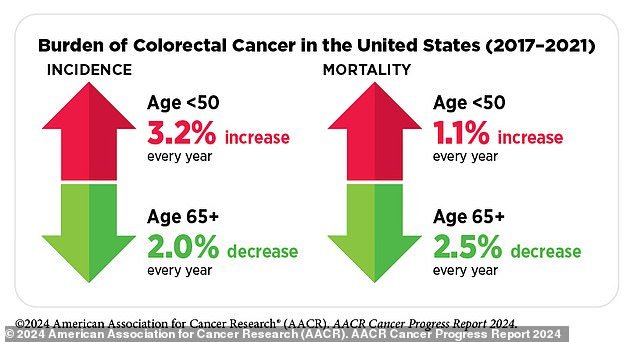
Overall, early-onset cancer cases, defined as those between the ages of 18 and 50, have been increasing in the United States since 1995.
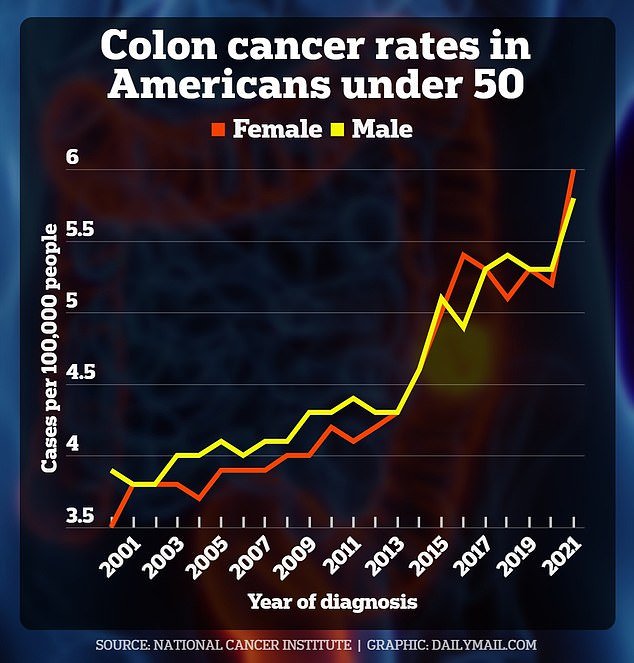
The latest NCI data on colorectal cancer only goes up to 2021, according to a new AACR report. AACR is separate from NCI, and is a publicly funded charity
The system, currently in use in eight US states, places a higher price on drinks made with added sugar.
Implementing this tax has significantly reduced the amount of sugary drinks consumed in areas, research from the Obesity Evidence Hub concluded.
After sugar, the researchers set their sights on alcohol.
Excessive alcohol consumption raises the risk of six different types of cancer (head and neck, throat, breast, bowel, liver and colon) and is linked to 5.4 percent of all cancers in the United States.
Young people who drank a lot of alcohol in adulthood increased their chances of developing colorectal cancer under the age of 50 by 1.5 times.
‘Unfortunately, awareness of the link between alcohol and cancer remains low,’ the report said.
Alcohol affects each part of the body differently, but in general, it can increase the risk of cancer by making it harder for our cells to respond to damage and change, making them more likely to become cancerous, according to Cancer Research UK.
Also, drinking alcohol can temporarily damage the cells in the mouth and throat, making them more susceptible to other cancer-causing chemicals, such as cigarette smoke.
All of these factors can increase a person’s chances of becoming overweight and obese.
Being overweight was associated with 7.6 percent of all cancers in the US. Obesity is on the rise in America – up 37 percent since 2000, to 41.9 percent in 2020.
There are 15 different types of cancer linked to being overweight or obese – from blood to brain to bladder.
Losing weight can be an effective way to reduce the risk of obesity-related cancers.
The report said that previous medical interventions to reduce cancer, such as weight-loss surgery, had been shown to be very effective – and they were testing whether new treatments such as Ozempic and Wegovy and they can help prevent cancer.
In addition to these daily habits, researchers said that other medical conditions may contribute to the increase in cancer in young people.
This includes overuse of antibiotics.

Dr Foti, AACR chief executive, said he hoped this would encourage government investment in cancer research, which he said had begun to see ‘amazing progress’ in recent years.
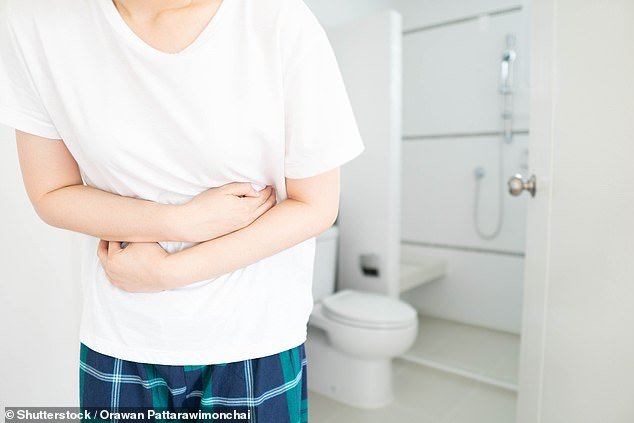
Early symptoms of colon cancer include changes in bowel habits, abdominal cramping, weight loss and fatigue. These are common symptoms of many other diseases as well, which means that the disease can be difficult to catch
Taking antibiotics for a long time can damage the unique biology of the intestinal system – known as the microbiome.
This layer of bacteria helps protect the gut against injury and in response to infection and illness, and can be damaged by long-term use of antibiotics. This may allow cancer to more easily set up camp in the colon, the researchers said
Studies have shown that people under the age of 50 taking antibiotics were 1.5 times more likely to develop colon cancer, while people over the age of 50 in the same situation were has only a 1.1 chance of developing the disease.
In addition to antibiotics, the report highlights the impact of missing vaccines for human papilloma virus, a highly contagious STD linked to head, neck, throat, cervical and oral cancers.
There is a series of vaccines available for teenagers to prevent HPV, and they have been shown to be 100 percent effective in preventing girls from developing cervical cancer later in life.
But in the US, only 38 percent of children have received one or more doses of this vaccine, compared to 76 percent of children in the UK and 84 percent in Australia.
Finally, the AACR report highlighted the risk of exposure to chemicals in the environment, but did not specify which chemicals.
For example, a recent study from the National Cancer Institute linked drinking water containing nitrates, a chemical produced when compost is exposed to the air, to colon cancer.
Despite these problems, Dr Margaret Foti, Director of the AACR, said that their report, shows that in many other groups, cancer prevention is still working. This year alone, US regulators have approved 15 new cancer treatments.
He said he wants these results to help encourage more national investment in research.
Dr Foti said: It is our hope that the 14th year of the year will help increase knowledge about cancer and raise awareness of the urgency of federal support for scientific and medical research.
#lifestyle #factors #driving #cancer #epidemic #young #people #major #report